What is the heat pump?
release time:
2023-08-07
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a source of heat to a destination called a heat sink. Heat pumps move thermal energy in the opposite direction of spontaneous heat transfer, by absorbing heat from a cold space and releasing it to a warmer one. A heat pump uses a small amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink.
So, what is the heat pump? The heat pump is part of a home heating and cooling system and is installed outside your home. Like an air conditioner such as central air, it can cool your home, but it’s also capable of providing heat. In cooler months, a heat pump pulls heat from the cold outdoor air and transfers it indoors, and in warmer months, it pulls heat out of indoor air to cool your home. They are powered by electricity and transfer heat using refrigerant to provide comfort all year round. Because they are able to both heat and cool a residence, homeowners may not need to install separate systems to heat their homes. In colder climates, an electric heat strip can be added to the indoor fan coil for additional capabilities. Heat pumps do not burn fossil fuels like furnaces do, making them more environmentally friendly.
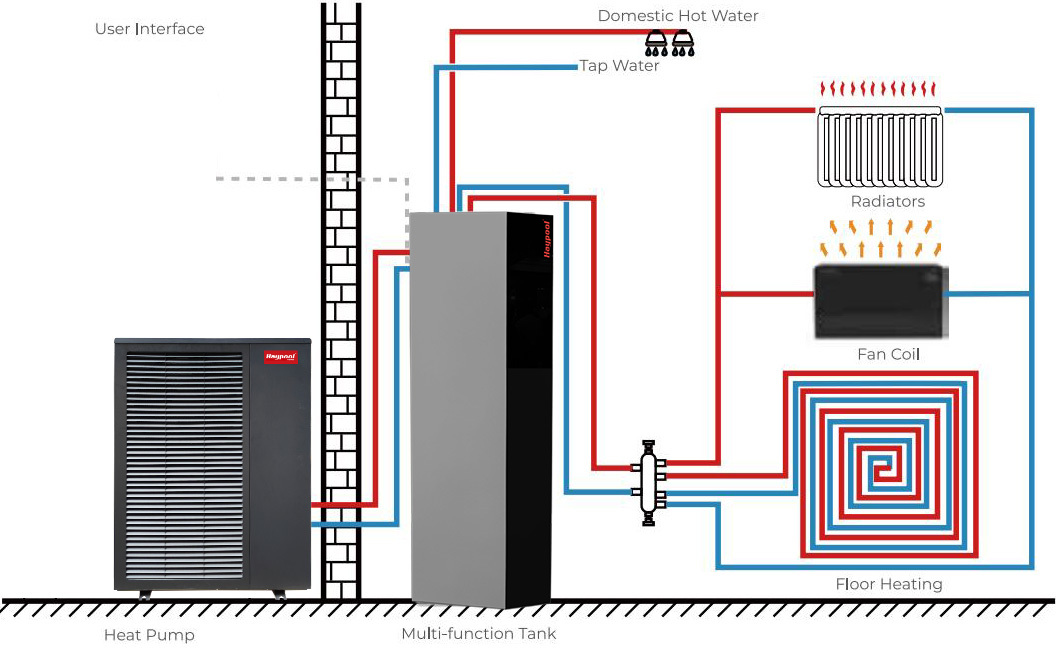
Some key things to know about heat pumps:
1、They can be used for both heating and cooling. In heating mode, they absorb heat from outside air or the ground and pump it indoors. In cooling mode, they work in reverse, absorbing heat from inside air and releasing it outdoors or into the ground.
2、They move heat rather than generate it. Heat pumps don't produce heat, they just transfer existing heat. This makes them more energy efficient than furnaces which must generate heat through combustion.
3、They run on electricity but are more efficient than resistive electric heating. Heat pumps can provide 2-3 times more heat energy per kWh than a resistive electric heater.
4、Common types include air-source heat pumps,ground-source heat pumps, and ductless mini-split heat pumps. Each has advantages and tradeoffs.
5、Heat pumps work more efficiently the closer the indoor and outdoor temperatures are. Performance declines in very cold or very hot weather.
Homeowners who need a new heating or cooling system may want to consider the type of climate they live in before purchasing a heat pump system. Heat pumps are more common in temperate climates, where temperatures don't usually drop below freezing. In extremely cold areas, they can also be used in combination with gas stoves to enable energy-efficient heating on all but the coldest days. When the outside temperature drops too low for the heat pump to operate efficiently, the system switches the gas stove to generate heat. This system is often referred to as a dual-fuel system - it is very energy efficient and affordable.

HAYPOL
Add:Building 5, Koneng Industrial Park, No.39 Zhenghe South Road, New Town Community, Leliu Street, Shunde District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province, China
Tel: 400-8642-688 / 0757-22394710
Cell / Whatsapp :+86 13794052160


 haypol@haypol.com
haypol@haypol.com

 +8613794052160
+8613794052160